DESIGN
Bollards are designed in accordance to acknowledged international standards such as BS 6349 part 4 and PIANC guidelines. Every bollard is considered a minimum factor of safety 1.5 against tensile or 3.0 against fracture, whichever is stricter. With numeric calculation and finite element analysis method, the bollards are optimized to have maximum strength with long working life.
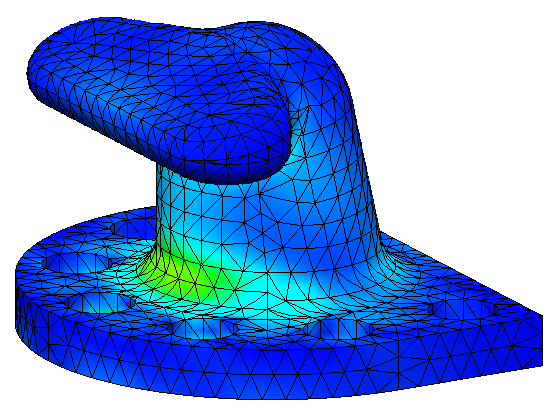
MATERIAL
Common bollards are provided with Ductile Cast Iron (Spheroidal Graphite Iron) or Cast Steel. Both materials can satisfy the majority of application, while there are still differences between them.
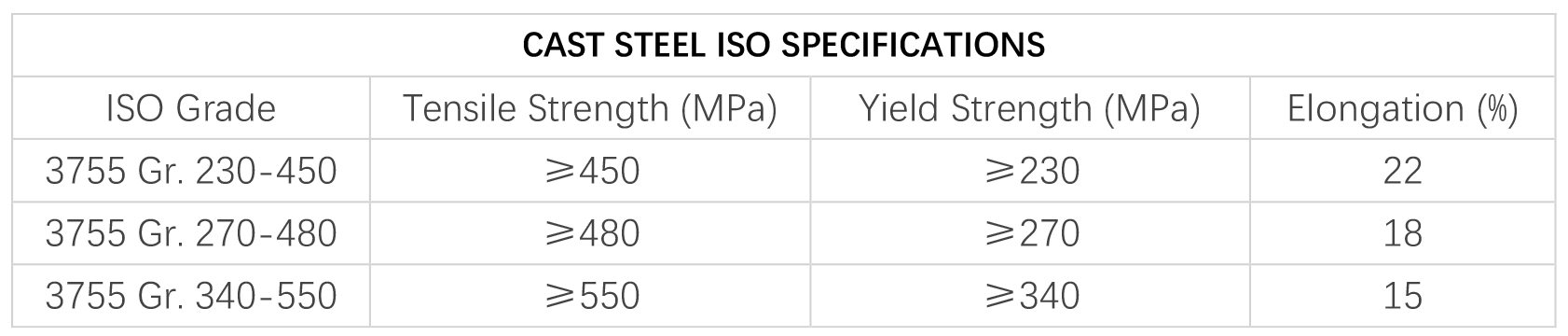
Cast steel has better ductility compare to ductile cast iron. That gives wider structrual margin in the event of overload situation.
Due to it properties, minor defect or damage are endurable and can be easily repaired by welding. Cast steel bollard also can be welded to the steel supporting structure.
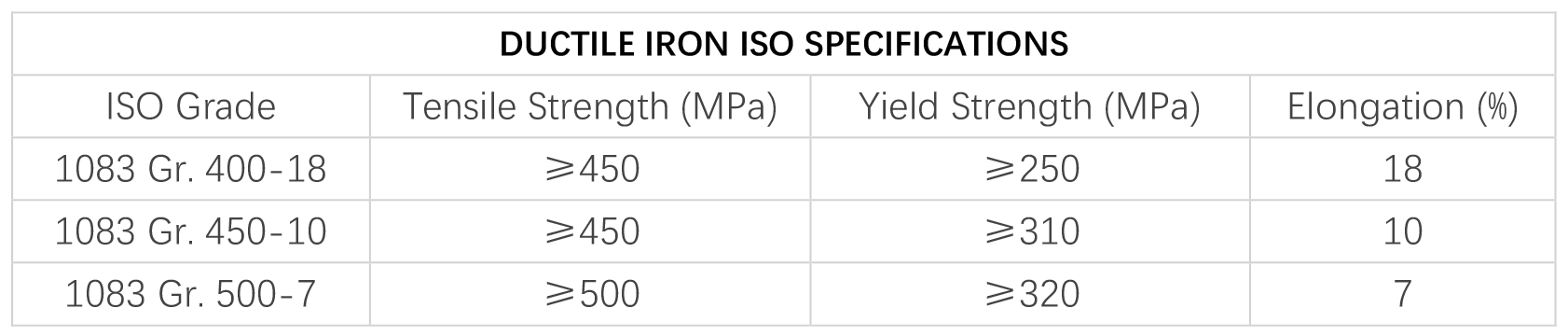
Ductile iron is more corrosion resistant than cast steel. It can tolerate ninor coating damage so lower maintenance cost is needed. Good strength performance and corrosion resistant attribute make it a ideal material for bollards.
COATING
To reduce corrosion and improve surface quality, coating is sinigficant for mooring bollards.
Bollards are supplied C5M(ISO 12944-2) standard coating, which is able to protect the bollards against very high corrosive marine atmosphere.
Typical coating procedures are as follows:
Surface preparation: Shot blasting to degree of cleanliness Sa 2.5 (ISO 8501)
Primer Coat: 1 layer of zinc rich epoxy primer >80 microns
Mid-Coat: 2 layers of epoxy paint >220 microns
Top Coat: 1 layer of polyurethane top coat >30 microns
Total DFT will greater than 350 microns.